About me
I am Data Scientist in Translational Medicine at Novartis. My work focuses on improving the probability of success of drug development by using machine learning and heterogeneous health data, including continuous measurement from wearable devices, compound descriptors, clinical trial reports.
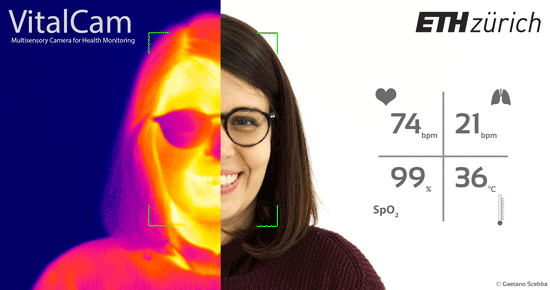
Prior to joining Novartis, I was a doctoral researcher in biomedical engineering at ETH Zurich, where I worked in close collaboration with students and medical researchers from Balgrist Clinic and University Hospital Zurich, on advancing physiological monitoring by utilizing machine learning and data from cameras and wearable devices. I hold a PhD in Biomedical Engineering (2021) from ETH Zurich, Switzerland, a MSc in Biomedical Engineering (2016) from Polytechnic University of Milan, Italy and a BSc in Biomedical Engineering (2013) from University of Pisa, Italy.